A Comparison Between Pyrolysis Plants and Traditional Incineration Techniques
The management of waste materials is a pressing global issue, with significant implications for environmental sustainability and public health. Traditional incineration techniques have long been used to dispose of waste, but in recent years, pyrolysis plants have emerged as an alternative technology with potential advantages. In this article, we will compare pyrolysis plants and traditional incineration techniques in terms of their environmental impact, resource recovery, and energy efficiency.
I. Environmental Impact: Emissions and Residue
- Pyrolysis Plants: Minimal Emissions and Residue
Pyrolysis plant offers a significant advantage in terms of environmental impact. The absence of oxygen during the pyrolysis process minimizes the formation of harmful gases and reduces the emission of pollutants. Additionally, the solid residue generated, known as char, is typically inert and contains a lower concentration of heavy metals compared to incineration ash. This char can be used as a valuable resource for applications such as soil amendment or carbon black production.
- Traditional Incineration: Emissions and Ash Disposal Challenges
Traditional incineration techniques result in higher emissions and a more complex residue management process. The emission control systems used in incinerators help mitigate air pollution, but they cannot completely eliminate the release of pollutants. Moreover, proper treatment and disposal of the generated ash are necessary to prevent contamination of soil and water bodies.
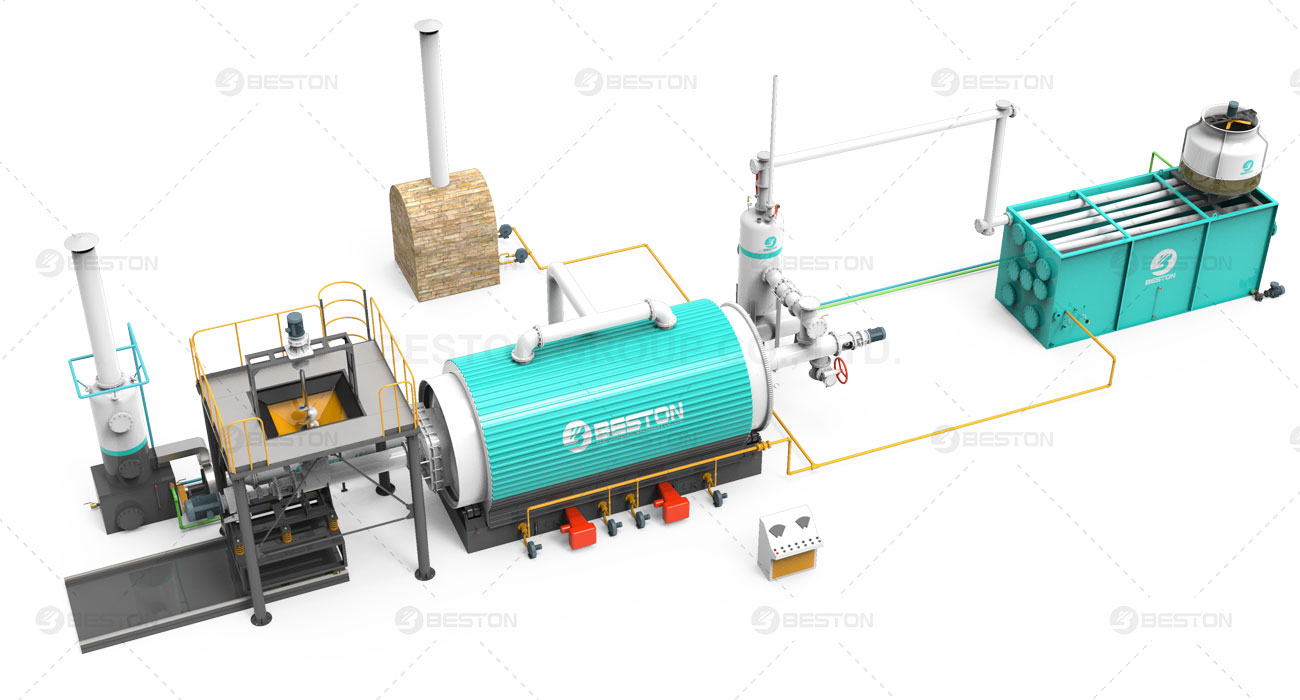

II. Resource Recovery: Energy and Material Utilization
- Pyrolysis Plants: Energy and Material Extraction
Pyrolysis plants excel in resource recovery as they enable the extraction of valuable energy and materials from waste. For example, through the tyre to oil plant, various products are obtained, including pyrolysis oil, pyrolysis gas, and char. Pyrolysis oil can be used as a renewable energy source or processed into fuels, while pyrolysis gas can be utilized for heat and power generation. The char produced can be utilized in various applications, reducing the need for virgin resources.
- Traditional Incineration: Focus on Energy Generation
Traditional incineration primarily focuses on energy generation through the combustion of waste. While energy recovery is a positive aspect, the potential for material extraction and resource reuse is limited. The ash generated during incineration may contain residual metals, making its utilization challenging and often requiring separate treatment processes.
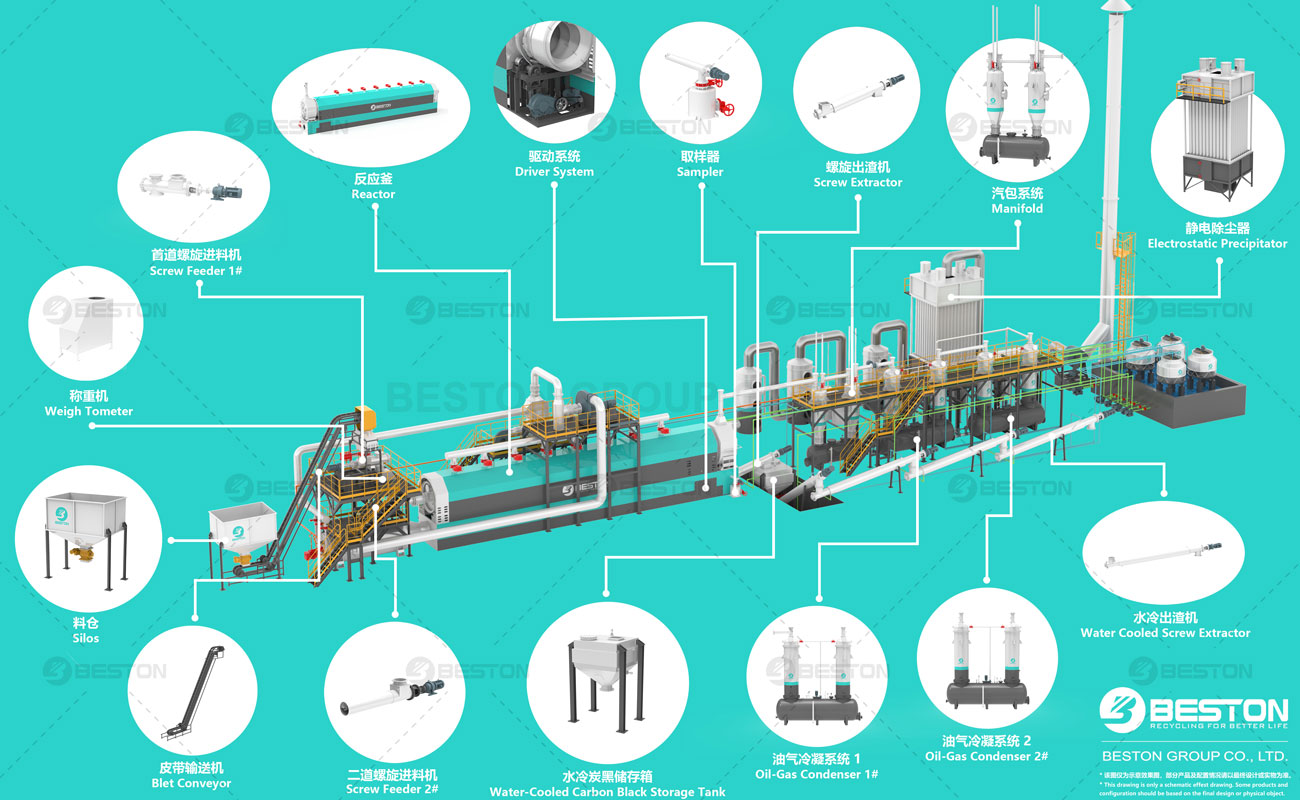
III. Energy Efficiency: Heat Recovery and Overall Efficiency
- Pyrolysis Plants: Heat Recovery and Synergies
The thermal desorption unit offers opportunities for efficient heat recovery. The heat generated during the pyrolysis process can be utilized internally to sustain the process or externally for district heating or industrial purposes. By maximizing heat recovery and establishing synergies with other processes, the overall energy efficiency of pyrolysis plants can be significantly improved.
- Traditional Incineration: Focus on Heat Generation
Traditional incineration focuses on heat generation through the combustion of waste, with limited opportunities for heat recovery. The energy produced is typically utilized for electricity generation or district heating. However, the overall energy efficiency of incineration techniques is lower compared to pyrolysis plants, as the potential for resource recovery and utilization is not fully realized.
If you want to know more details, please see the website: Beston Group.